|
I am Co-Founder and Chief Scientist at Nuance Labs. My research focuses on multimodal AI at the intersection of audio and video. Previously, I was a Senior AI/ML Researcher at Apple. I received my Ph.D. from the Laboratory for Information & Decision Systems at MIT, where I was advised by Caroline Uhler. During my Ph.D., I worked with leading researchers from Apple, Niantic Labs, Meta Reality Labs, Bosch Center for AI, and Adobe Research. Email / CV / Google Scholar |

|
|
Research Topics: all / multimodal learning / audio-visual learning / speech recognition / generative modeling / computational biology / optimal transport / causal inference |

|
Sanjoy Chowdhury, Karren D Yang, Xudong Liu, Fartash Faghri, Pavan Kumar Anasosalu Vasu, Oncel Tuzel, Dinesh Manocha, Chun-Liang Li, Raviteja Vemulapalli arXiv, 2025 We introduce AMUSE, a benchmark for evaluating multimodal large language models on agentic multi-speaker audio-visual reasoning, and propose RAFT, a data-efficient agentic alignment framework achieving up to 39.52% relative improvement. pdf | abstractRecent multimodal large language models (MLLMs) such as GPT-4o and Qwen3-Omni show strong perception but struggle in multi-speaker, dialogue-centric settings that demand agentic reasoning tracking who speaks, maintaining roles, and grounding events across time. These scenarios are central to multimodal audio-video understanding, where models must jointly reason over audio and visual streams in applications such as conversational video assistants and meeting analytics. We introduce AMUSE, a benchmark designed around tasks that are inherently agentic, requiring models to decompose complex audio-visual interactions into planning, grounding, and reflection steps. It evaluates MLLMs across three modes zero-shot, guided, and agentic and six task families, including spatio-temporal speaker grounding and multimodal dialogue summarization. Across all modes, current models exhibit weak multi-speaker reasoning and inconsistent behavior under both non-agentic and agentic evaluation. Motivated by the inherently agentic nature of these tasks and recent advances in LLM agents, we propose RAFT, a data-efficient agentic alignment framework that integrates reward optimization with intrinsic multimodal self-evaluation as reward and selective parameter adaptation for data and parameter efficient updates. Using RAFT, we achieve up to 39.52% relative improvement in accuracy on our benchmark. Together, AMUSE and RAFT provide a practical platform for examining agentic reasoning in multimodal models and improving their capabilities. |
|
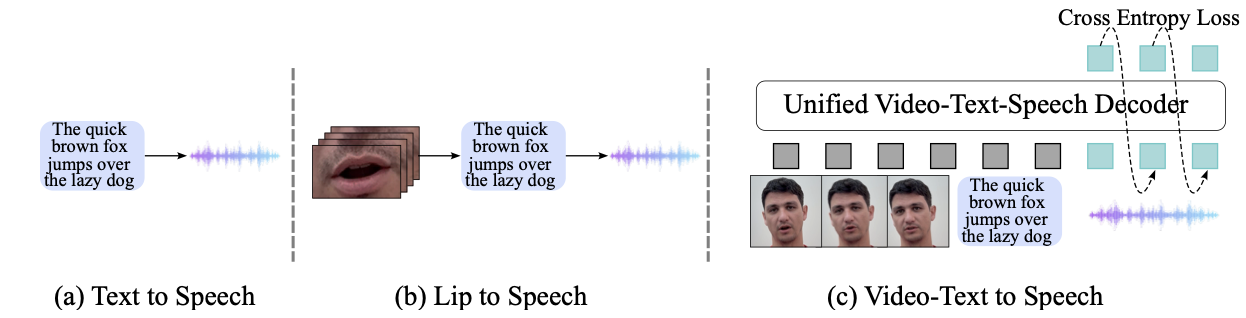
Akshita Gupta, Tatiana Likhomanenko, Karren Dai Yang, Richard He Bai, Zakaria Aldeneh, Navdeep Jaitly arXiv, 2024 We introduce Visatronic, a unified multimodal decoder-only transformer for video-text to speech synthesis that achieves 4.5% WER on LRS3 in zero-shot, outperforming prior methods trained on LRS3. pdf | abstract | demoThe rapid progress of foundation models and large language models (LLMs) has fueled significantly improvement in the capabilities of machine learning systems that benefit from mutlimodal input data. However, existing multimodal models are predominantly built on top of pre-trained LLMs, which can limit accurate modeling of temporal dependencies across other modalities and thus limit the model's ability to jointly process and leverage multimodal inputs. To specifically investigate the alignment of text, video, and speech modalities in LLM-style (decoder-only) models, we consider a simplified multimodal generation task, Video-Text to Speech (VTTS): speech generation conditioned on both its corresponding text and video of talking people. The ultimate goal is to generate speech that not only follows the text but also aligns temporally with the video and is consistent with the facial expressions. In this paper, we first introduce Visatronic, a unified multimodal decoder-only transformer model that adopts an LLM-style architecture to embed visual, textual, and speech inputs into a shared subspace, treating all modalities as temporally aligned token streams. Next, we carefully explore different token mixing strategies to understand the best way to propagate information from the steps where video and text conditioning is input to the steps where the audio is generated. We extensively evaluate Visatronic on the challenging VoxCeleb2 dataset and demonstrate zero-shot generalization to LRS3, where Visatronic, trained on VoxCeleb2, achieves a 4.5% WER, outperforming prior SOTA methods trained only on LRS3, which report a 21.4% WER. Additionally, we propose a new objective metric, TimeSync, specifically designed to measure phoneme-level temporal alignment between generated and reference speech, further ensuring synchronization quality. |
|
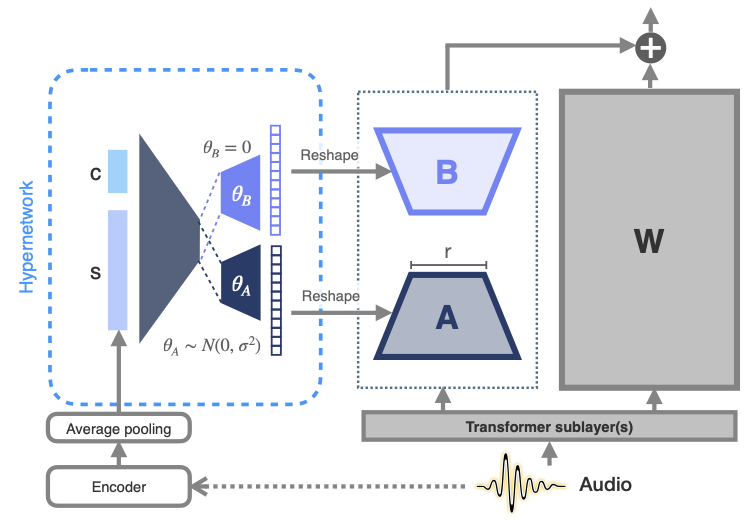
Max Müller-Eberstein, Dianna Yee, Karren Yang, Gautam Varma Mantena, Colin Lea Transactions of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Vol. 12, 2024 We propose meta-learned hypernetworks that generate utterance-level adaptations on-the-fly for personalizing ASR to diverse atypical speech, achieving 75.2% relative WER reduction using 0.1% of the parameter budget. pdf | abstractParameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) for personalizing automatic speech recognition (ASR) has recently shown promise for adapting general population models to atypical speech. However, these approaches assume a priori knowledge of the atypical speech disorder being adapted for—the diagnosis of which requires expert knowledge that is not always available. Even given this knowledge, data scarcity and high inter-/intra-speaker variability further limit the effectiveness of traditional fine-tuning. To circumvent these challenges, we first identify the minimal set of model parameters required for ASR adaptation. Our analysis of each individual parameter's effect on adaptation performance allows us to reduce Word Error Rate (WER) by half while adapting 0.03% of all weights. Alleviating the need for cohort-specific models, we next propose the novel use of a meta-learned hypernetwork to generate highly individualized, utterance-level adaptations on-the-fly for a diverse set of atypical speech characteristics. Evaluating adaptation at the global, cohort, and individual-level, we show that hypernetworks generalize better to out-of-distribution speakers, while maintaining an overall relative WER reduction of 75.2% using 0.1% of the full parameter budget. |
|
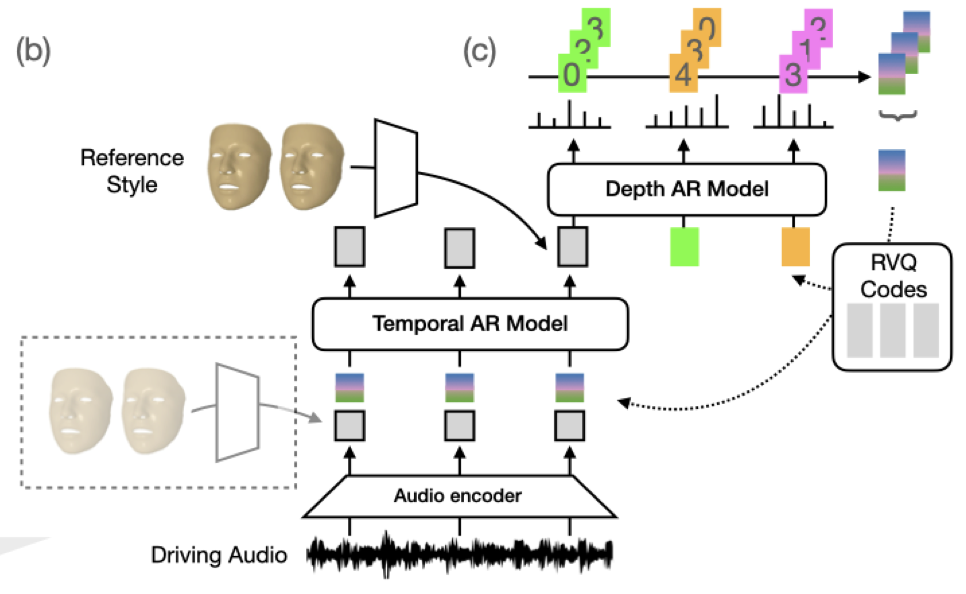
Karren D Yang, Anurag Ranjan, Jen-Hao Rick Chang, Raviteja Vemulapalli, Oncel Tuzel CVPR, 2024 We propose large-scale benchmarks and a probabilistic model for speech-driven 3D facial motion synthesis that achieves both diversity and fidelity, with applications to unseen speaker style transfer and improving downstream audio-visual models. pdf | abstractWe consider the task of animating 3D facial geometry from speech signal. Existing works are primarily deterministic, focusing on learning a one-to-one mapping from speech signal to 3D face meshes on small datasets with limited speakers. While these models can achieve high-quality lip articulation for speakers in the training set, they are unable to capture the full and diverse distribution of 3D facial motions that accompany speech in the real world. Importantly, the relationship between speech and facial motion is one-to-many, containing both inter-speaker and intra-speaker variations, and necessitating a probabilistic approach. In this paper, we identify and address key challenges that have so far limited the development of probabilistic models: lack of datasets and metrics that are suitable for training and evaluating them, as well as the difficulty of designing a model that generates diverse results while remaining faithful to a strong conditioning signal as speech. We first propose large-scale benchmark datasets and metrics suitable for probabilistic modeling. Then, we demonstrate a probabilistic model that achieves both diversity and fidelity to speech, outperforming other methods across the proposed benchmarks. Finally, we showcase useful applications of probabilistic models trained on these large-scale datasets: we can generate diverse speech-driven 3D facial motion that matches unseen speaker styles extracted from reference clips; and our synthetic meshes can be used to improve the performance of downstream audio-visual models. |
|
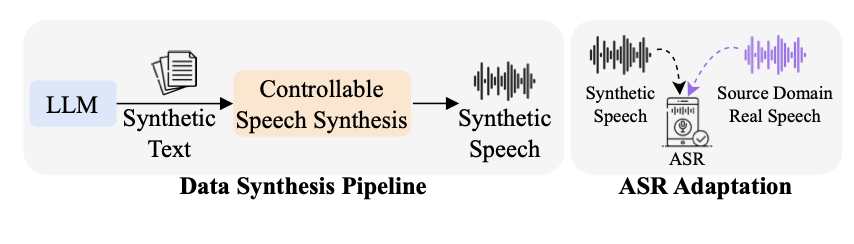
Hsuan Su, Ting-Yao Hu, Hema Swetha Koppula, Raviteja Vemulapalli, Jen-Hao Rick Chang, Karren Yang, Gautam Varma Mantena, Oncel Tuzel ICASSP, 2024 We propose a data synthesis pipeline using LLMs and controllable speech synthesis to adapt ASR models to new domains without any target-domain data, achieving 28% relative WER improvement. pdf | abstractWhile Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) systems are widely used in many real-world applications, they often do not generalize well to new domains and need to be fine-tuned on data from these domains. However, target-domain data usually are not readily available in many scenarios. In this paper, we propose a new strategy for adapting ASR models to new target domains without any text or speech from those domains. To accomplish this, we propose a novel data synthesis pipeline that uses a Large Language Model (LLM) to generate a target domain text corpus, and a state-of-the-art controllable speech synthesis model to generate the corresponding speech. We propose a simple yet effective in-context instruction fine-tuning strategy to increase the effectiveness of LLM in generating text corpora for new domains. Experiments on the SLURP dataset show that the proposed method achieves an average relative word error rate improvement of 28% on unseen target domains without any performance drop in source domains. |
|
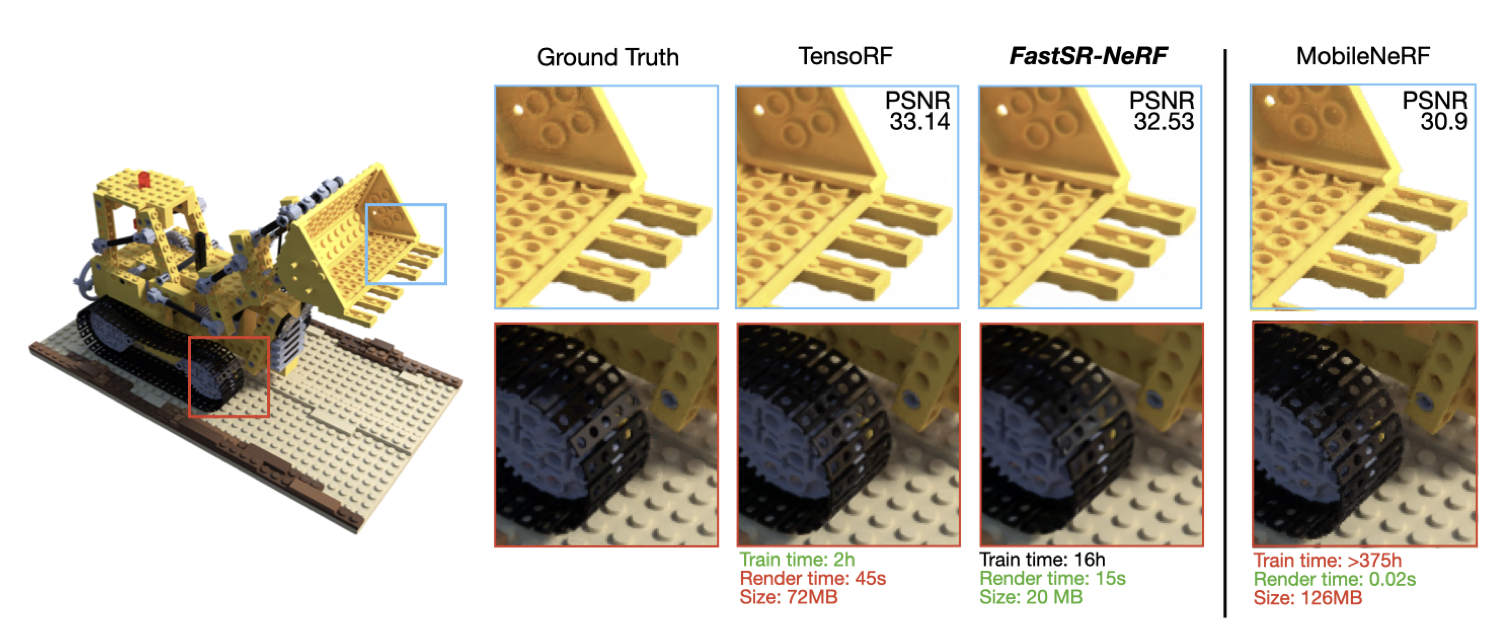
Chien-Yu Lin, Qichen Fu, Thomas Merth, Karren Yang, Anurag Ranjan WACV, 2024 (Oral Presentation) We build a simple NeRF + super-resolution pipeline that upscales NeRF outputs by 2-4x, increasing inference speed up to 18x on GPU and 12.8x on Apple M1 Pro, while training up to 23x faster than existing NeRF+SR methods. pdf | abstractSuper-resolution (SR) techniques have recently been proposed to upscale the outputs of neural radiance fields (NeRF) and generate high-quality images with enhanced inference speeds. However, existing NeRF+SR methods increase training overhead by using extra input features, loss functions, or expensive training procedures such as knowledge distillation. In this paper, we aim to leverage SR for efficiency gains without costly training or architectural changes. Specifically, we build a simple NeRF+SR pipeline that directly combines existing modules, and we propose a lightweight augmentation technique, random patch sampling, for training. Compared to existing NeRF+SR methods, our pipeline mitigates the SR computing overhead and can be trained up to 23x faster, making it feasible to run on consumer devices such as the Apple MacBook. Experiments show that our pipeline can upscale NeRF outputs by 2-4x while maintaining high quality, increasing inference speeds by up to 18x on an NVIDIA V100 GPU and 12.8x on an M1 Pro chip. We conclude that SR can be a simple but effective technique for improving the efficiency of NeRF models for consumer devices. |
|
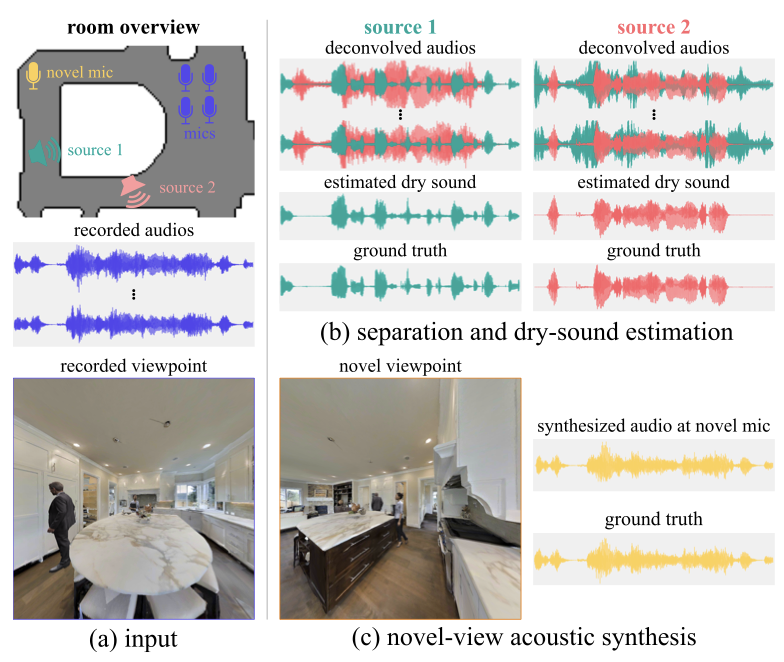
Byeongjoo Ahn, Karren Yang, Brian Hamilton, Jonathan Sheaffer, Anurag Ranjan, Miguel Sarabia, Oncel Tuzel, Jen-Hao Rick Chang arXiv, 2023 We combine blind audio recordings with 3D scene information to estimate sound anywhere in a scene, jointly tackling source localization, separation, and dereverberation. pdf | abstract | codeWe investigate the benefit of combining blind audio recordings with 3D scene information for novel-view acoustic synthesis. Given audio recordings from 2-4 microphones and the 3D geometry and material of a scene containing multiple unknown sound sources, we estimate the sound anywhere in the scene. We identify the main challenges of novel-view acoustic synthesis as sound source localization, separation, and dereverberation. While naively training an end-to-end network fails to produce high-quality results, we show that incorporating room impulse responses (RIRs) derived from 3D reconstructed rooms enables the same network to jointly tackle these tasks. Our method outperforms existing methods designed for the individual tasks, demonstrating its effectiveness at utilizing 3D visual information. In a simulated study on the Matterport3D-NVAS dataset, our model achieves near-perfect accuracy on source localization, a PSNR of 26.44dB and a SDR of 14.23dB for source separation and dereverberation, resulting in a PSNR of 25.55 dB and a SDR of 14.20 dB on novel-view acoustic synthesis. We release our code and model on our project website. |
|
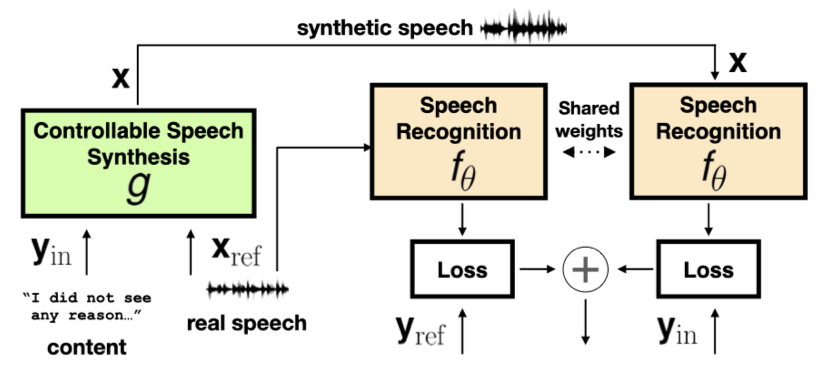
Karren Yang, Ting-Yao Hu, Jen-Hao Rick Chang, Hema Swetha Koppula, Oncel Tuzel ICASSP, 2023 We study when and why synthetic data is effective for ASR personalization, finding that text content rather than style drives speaker adaptation, leading to a content-based data selection strategy. pdf | abstractAdapting generic speech recognition models to specific individuals is a challenging problem due to the scarcity of personalized data. Recent works have proposed boosting the amount of training data using personalized text-to-speech synthesis. Here, we ask two fundamental questions about this strategy: when is synthetic data effective for personalization, and why is it effective in those cases? To address the first question, we adapt a state-of-the-art automatic speech recognition (ASR) model to target speakers from four benchmark datasets representative of different speaker types. We show that ASR personalization with synthetic data is effective in all cases, but particularly when (i) the target speaker is underrepresented in the global data, and (ii) the capacity of the global model is limited. To address the second question of why personalized synthetic data is effective, we use controllable speech synthesis (CSS) to generate speech with varied styles and content. Surprisingly, we find that the text content of the synthetic data, rather than style, is important for speaker adaptation. These results lead us to propose a data selection strategy for ASR personalization based on speech content. |
|
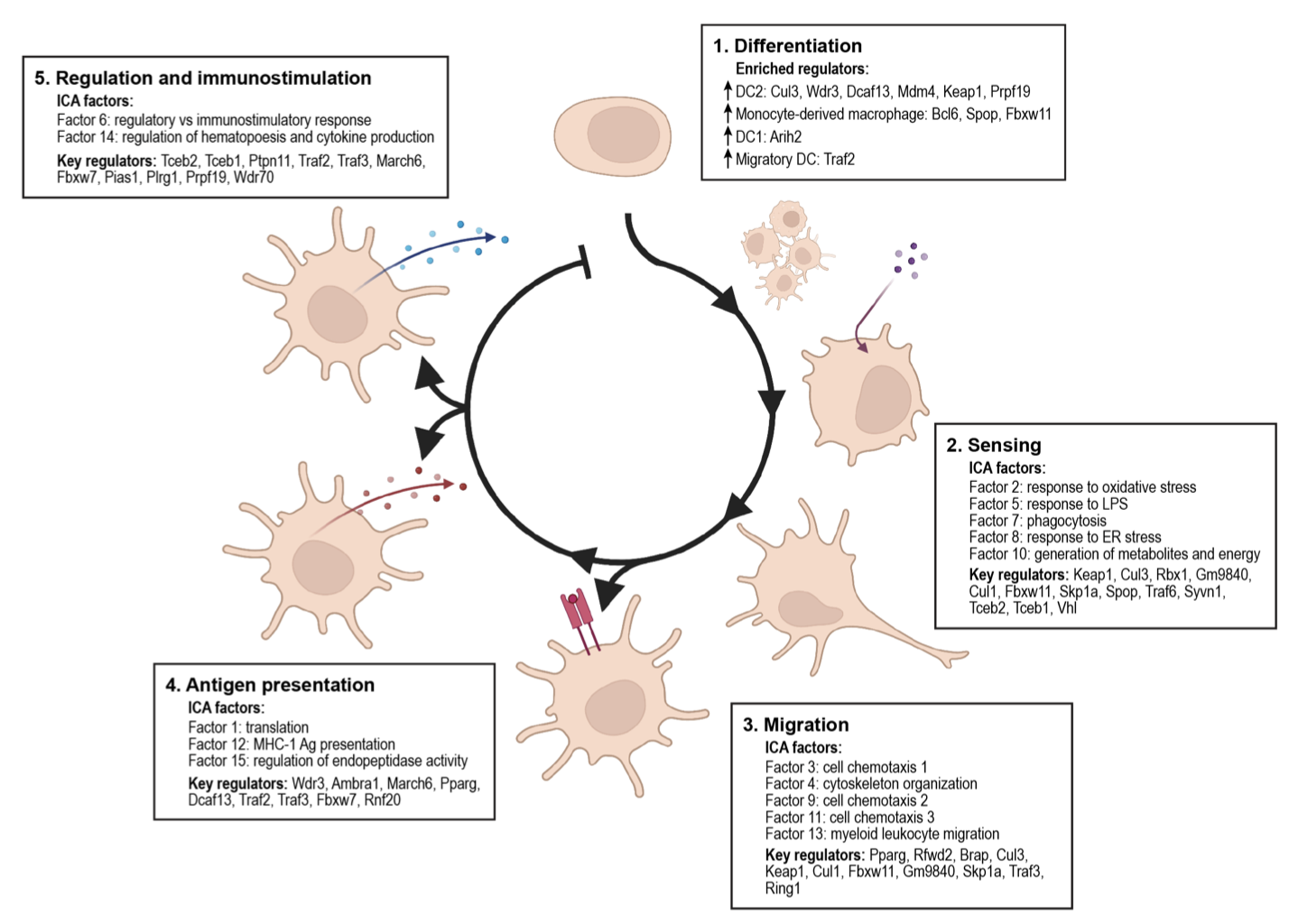
Kathryn Geiger-Schuller, Basak Eraslan, Olena Kuksenko, Kushal K Dey, Karthik A Jagadeesh, Pratiksha I Thakore, Ozge Karayel, Andrea R Yung, Anugraha Rajagopalan, Ana M Meireles, Karren Dai Yang, Liat Amir-Zilberstein, Toni Delorey, Devan Phillips, Raktima Raychowdhury, Christine Moussion, Alkes L Price, Nir Hacohen, John G Doench, Caroline Uhler, Orit Rozenblatt-Rosen, Aviv Regev bioRxiv, 2023 Using Perturb-seq, we interrogated the function of 1,130 E3 ligases in the inflammatory response in dendritic cells, revealing co-functional modules and predicting outcomes of new genetic combinations with deep learning. pdf | abstractE3 ligases regulate key processes, but many of their roles remain unknown. Using Perturb-seq, we interrogated the function of 1,130 E3 ligases, partners and substrates in the inflammatory response in primary dendritic cells (DCs). Dozens impacted the balance of DC1, DC2, migratory DC and macrophage states and a gradient of DC maturation. Family members grouped into co-functional modules that were enriched for physical interactions and impacted specific programs through substrate transcription factors. E3s and their adaptors co-regulated the same processes, but partnered with different substrate recognition adaptors to impact distinct aspects of the DC life cycle. Genetic interactions were more prevalent within than between modules, and a deep learning model, comβVAE, predicts the outcome of new combinations by leveraging modularity. The E3 regulatory network was associated with heritable variation and aberrant gene expression in immune cells in human inflammatory diseases. Our study provides a general approach to dissect gene function. |
|
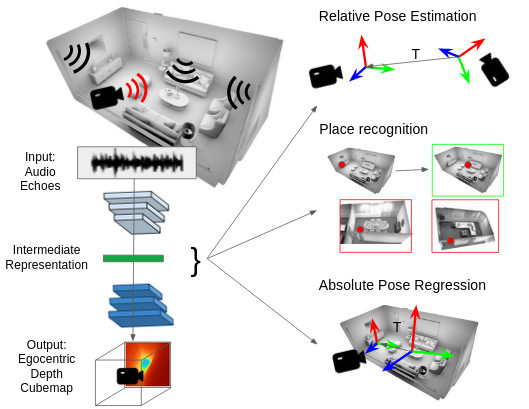
Karren Yang, Clément Godard, Eric Brachmann, Michael Firman ECCV, 2022 We use audio sensing to improve the performance of visual localization methods on three tasks: relative pose estimation, place recognition, and absolute pose regression. pdf | abstractIn this work, we show how to estimate a device's position and orientation indoors by echolocation, i.e., by interpreting the echoes of an audio signal that the device itself emits. Established visual localization methods rely on the device's camera and yield excellent accuracy if unique visual features are in view and depicted clearly. We argue that audio sensing can offer complementary information to vision for device localization, since audio is invariant to adverse visual conditions and can reveal scene information beyond a camera's field of view. We first propose a strategy for learning an audio representation that captures the scene geometry around a device using supervision transfer from vision. Subsequently, we leverage this audio representation to complement vision in three device localization tasks: relative pose estimation, place recognition, and absolute pose regression. Our proposed methods outperform state-of-the-art vision models on new audio-visual benchmarks for the Replica and Matterport3D datasets. |
|
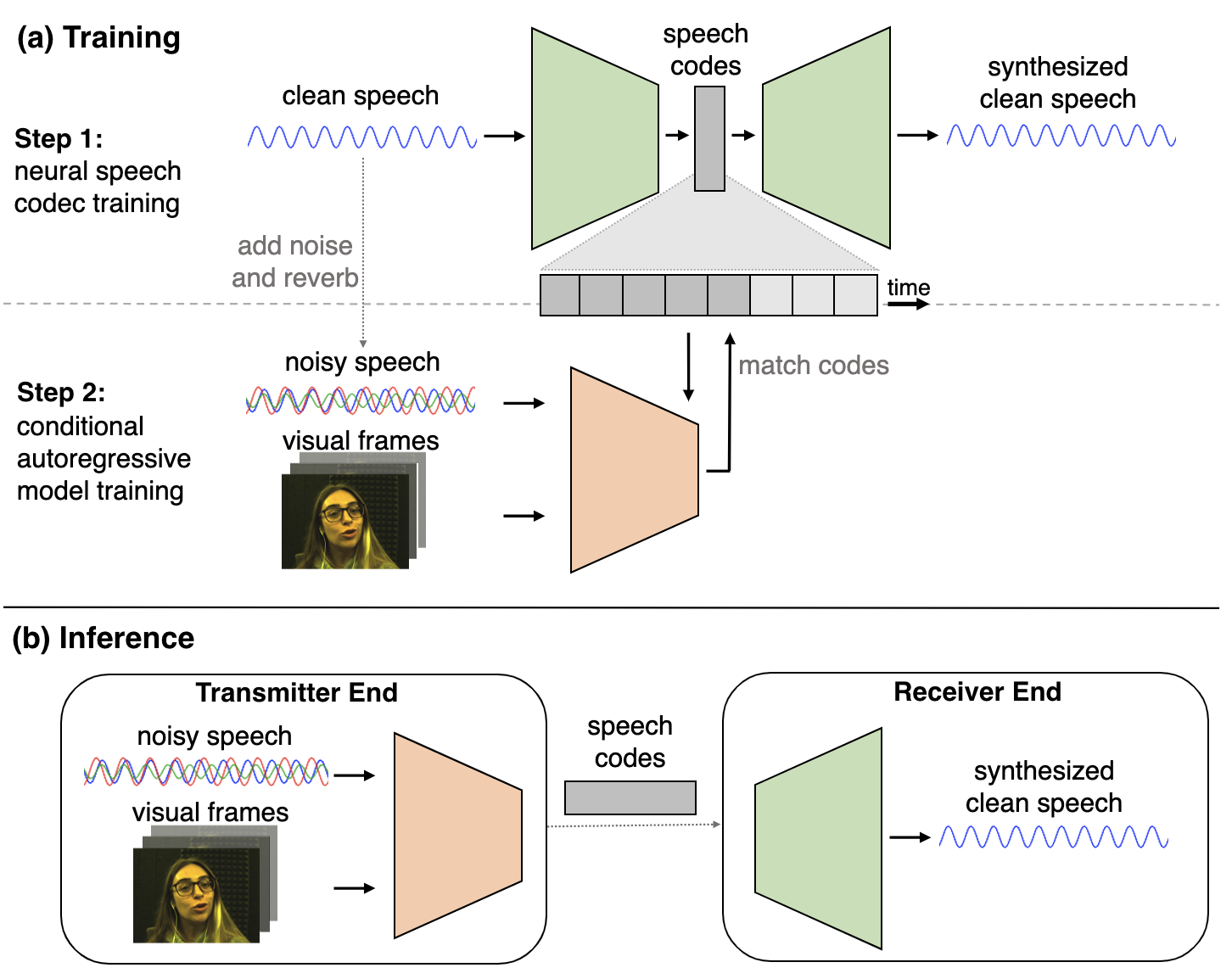
Karren Yang, Dejan Markovic, Steven Krenn, Vasu Agrawal, Alexander Richard CVPR, 2022 (Oral Presentation) We perform visual speech enhancement by using audio-visual speech cues to generate the codes of a neural speech codec, enabling efficient synthesis of clean, realistic speech from noisy signals. pdf | abstract | video | datasetSince facial actions such as lip movements contain significant information about speech content, it is not surprising that audio-visual speech enhancement methods are more accurate than their audio-only counterparts. Yet, state-of-the-art approaches still struggle to generate clean, realistic speech without noise artifacts and unnatural distortions in challenging acoustic environments. In this paper, we propose a novel audio-visual speech enhancement framework for high-fidelity telecommunications in AR/VR. Our approach leverages audio-visual speech cues to generate the codes of a neural speech codec, enabling efficient synthesis of clean, realistic speech from noisy signals. Given the importance of speaker-specific cues in speech, we focus on developing personalized models that work well for individual speakers. We demonstrate the efficacy of our approach on a new audio-visual speech dataset collected in an unconstrained, large vocabulary setting, as well as existing audio-visual datasets, outperforming speech enhancement baselines on both quantitative metrics and human evaluation studies. Please see the supplemental video for qualitative results. |
|
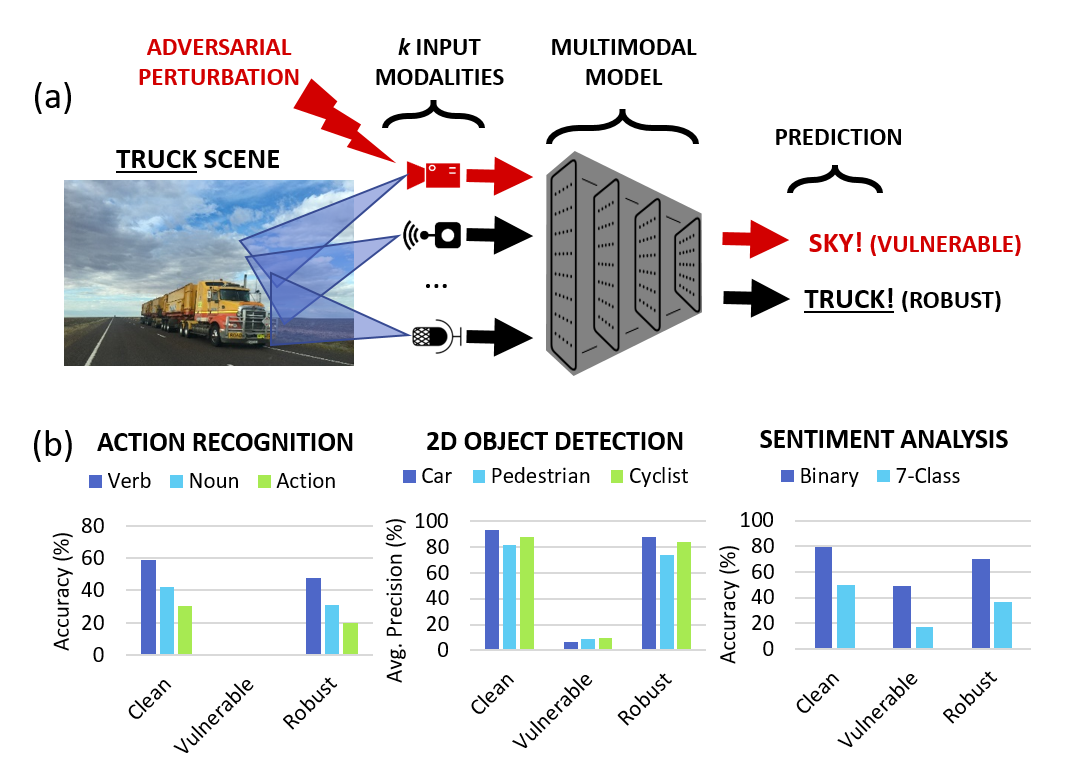
Karren Yang, Wan-Yi Lin, Manash Barman, Filipe Condessa, Zico Kolter CVPR, 2021 We study the robustness of multimodal models on three tasks-- action recognition, object detection, and sentiment analysis-- and develop a robust fusion strategy that protects against worst-case errors caused by a single modality. pdf | abstractBeyond achieving high performance across many vision tasks, multimodal models are expected to be robust to single-source faults due to the availability of redundant information between modalities. In this paper, we investigate the robustness of multimodal neural networks against worst-case (i.e., adversarial) perturbations on a single modality. We first show that standard multimodal fusion models are vulnerable to single-source adversaries: an attack on any single modality can overcome the correct information from multiple unperturbed modalities and cause the model to fail. This surprising vulnerability holds across diverse multimodal tasks and necessitates a solution. Motivated by this finding, we propose an adversarially robust fusion strategy that trains the model to compare information coming from all the input sources, detect inconsistencies in the perturbed modality compared to the other modalities, and only allow information from the unperturbed modalities to pass through. Our approach significantly improves on state-of-the-art methods in single-source robustness, achieving gains of 7.8-25.2% on action recognition, 19.7-48.2% on object detection, and 1.6-6.7% on sentiment analysis, without degrading performance on unperturbed (i.e., clean) data. |
|
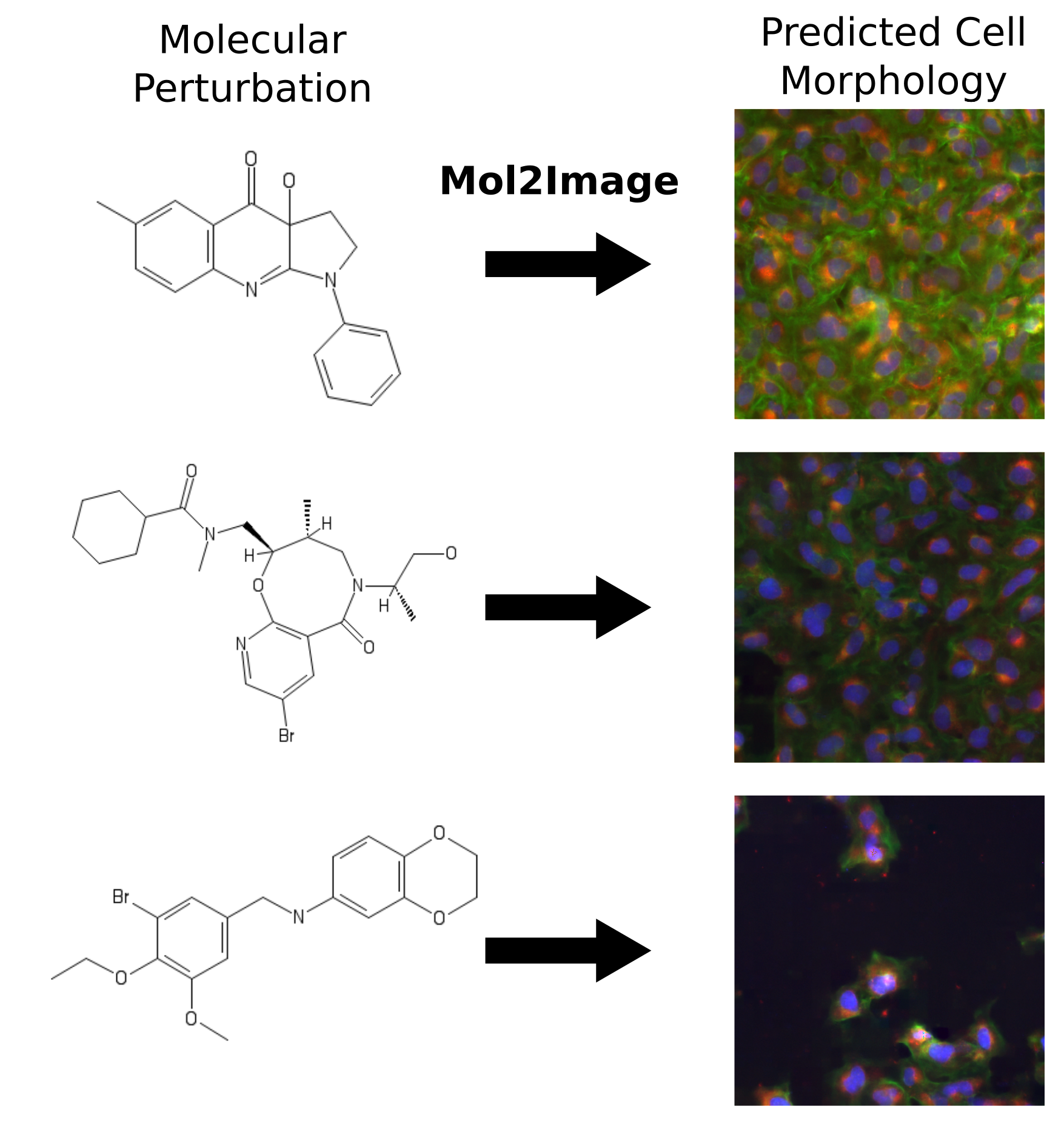
Karren Yang, Samuel Goldman, Wengong Jin, Alex Lu, Regina Barzilay, Tommi Jaakkola, Caroline Uhler CVPR, 2021 We build a molecule-to-image synthesis model that predicts the biological effects of molecular treatments on cell microscopy images. pdf | abstract | codeIn this paper, we aim to synthesize cell microscopy images under different molecular interventions, motivated by practical applications to drug development. Building on the recent success of graph neural networks for learning molecular embeddings and flow-based models for image generation, we propose Mol2Image: a flow-based generative model for molecule to cell image synthesis. To generate cell features at different resolutions and scale to high-resolution images, we develop a novel multi-scale flow architecture based on a Haar wavelet image pyramid. To maximize the mutual information between the generated images and the molecular interventions, we devise a training strategy based on contrastive learning. To evaluate our model, we propose a new set of metrics for biological image generation that are robust, interpretable, and relevant to practitioners. We show quantitatively that our method learns a meaningful embedding of the molecular intervention, which is translated into an image representation reflecting the biological effects of the intervention. |
|
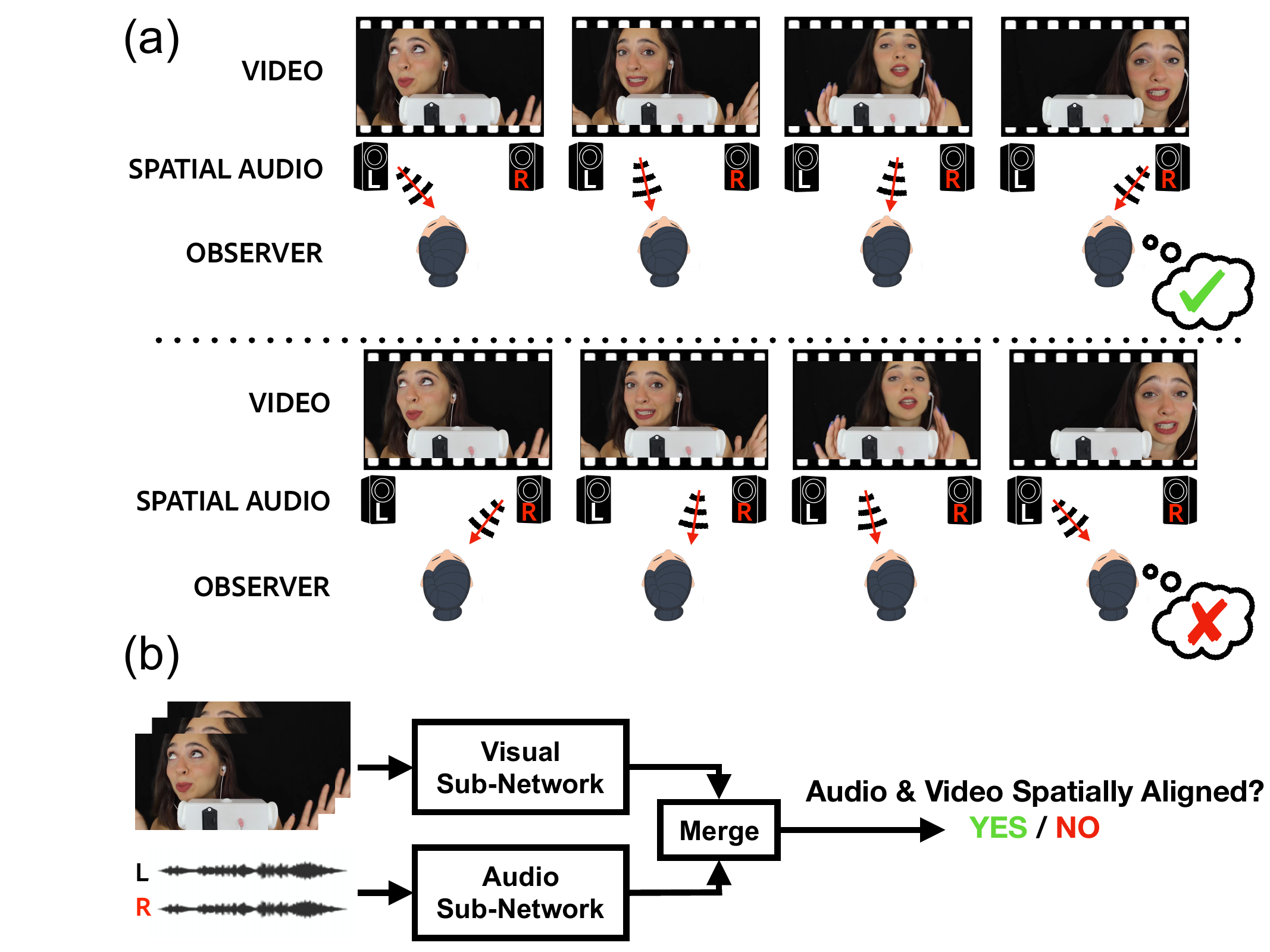
Karren Yang, Justin Salamon, Bryan Russell CVPR, 2020 (Oral Presentation) We leverage spatial correspondence between audio and vision in videos for self-supervised representation learning and apply the learned representations to three downstream tasks: sound localization, audio spatialization, and audio-visual sound separation. pdf | abstract | project website | dataset | demo codeSelf-supervised audio-visual learning aims to capture useful representations of video by leveraging correspondences between visual and audio inputs. Existing approaches have focused primarily on matching semantic information between the sensory streams. We propose a novel self-supervised task to leverage an orthogonal principle: matching spatial information in the audio stream to the positions of sound sources in the visual stream. Our approach is simple yet effective. We train a model to determine whether the left and right audio channels have been flipped, forcing it to reason about spatial localization across the visual and audio streams. To train and evaluate our model, we introduce a large-scale video dataset, YouTube-ASMR-300K, with spatial audio comprising over 900 hours of footage. We demonstrate that understanding spatial correspondence enables models to perform better on three audio-visual tasks, achieving quantitative gains over supervised and self-supervised baselines that do not leverage spatial audio cues. We also show how to extend our self-supervised approach to 360 degree videos with ambisonic audio. |
|
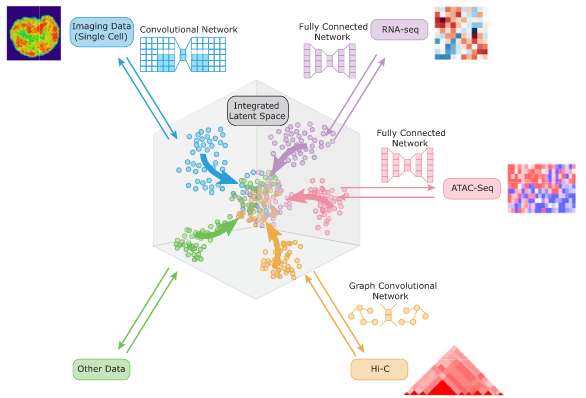
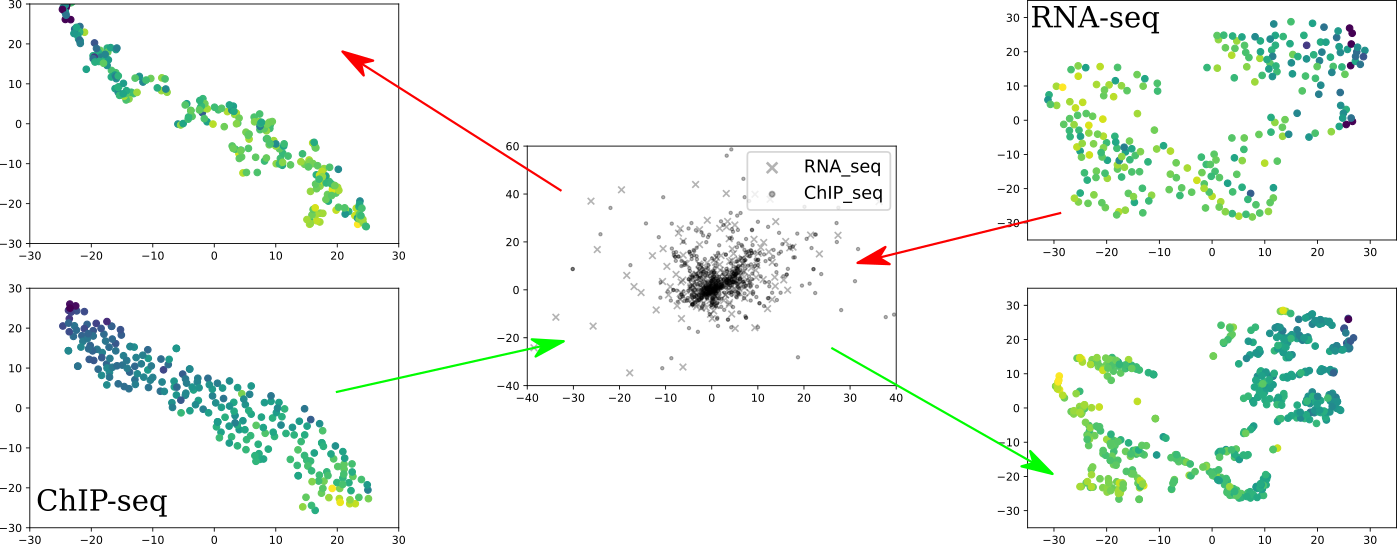
Karren Dai Yang*, Anastasiya Belyaeva*, Saradha Venkatachalapathy, Karthik Damodaran, Abigail Katcoff, Adityanarayanan Radhakrishnan, G. V. Shivashankar, Caroline Uhler Nature Communications 12, 31 (2021) We propose a framework for integrating and translating between different modalities of single-cell biological data by using autoencoders to map to a shared latent space. pdf | abstract | codeThe development of single-cell methods for capturing different data modalities including imaging and sequencing has revolutionized our ability to identify heterogeneous cell states. Different data modalities provide different perspectives on a population of cells, and their integration is critical for studying cellular heterogeneity and its function. While various methods have been proposed to integrate different sequencing data modalities, coupling imaging and sequencing has been an open challenge. We here present an approach for integrating vastly different modalities by learning a probabilistic coupling between the different data modalities using autoencoders to map to a shared latent space. We validate this approach by integrating single-cell RNA-seq and chromatin images to identify distinct subpopulations of human naive CD4+ T-cells that are poised for activation. Collectively, our approach provides a framework to integrate and translate between data modalities that cannot yet be measured within the same cell for diverse applications in biomedical discovery. |
|
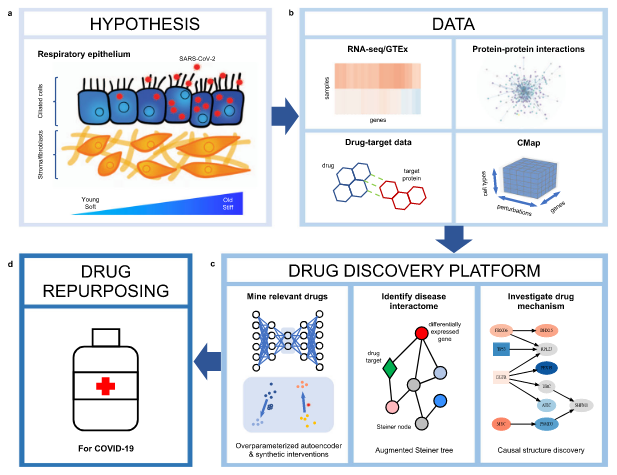
Anastasiya Belyaeva, Louis Cammarata, Adityanarayanan Radhakrishnan, Chandler Squires, Karren Yang, G. V. Shivashankar, Caroline Uhler Nature Communications 12, 1024 (2021) We integrate transcriptomic, proteomic, and structural data to identify candidate drugs and targets that affect the SARS-CoV-2 and aging pathways. pdf | abstractGiven the severity of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic, a major challenge is to rapidly repurpose existing approved drugs for clinical interventions. While a number of data-driven and experimental approaches have been suggested in the context of drug repurposing, a platform that systematically integrates available transcriptomic, proteomic and structural data is missing. More importantly, given that SARS-CoV-2 pathogenicity is highly age-dependent, it is critical to integrate aging signatures into drug discovery platforms. We here take advantage of large-scale transcriptional drug screens combined with RNA-seq data of the lung epithelium with SARS-CoV-2 infection as well as the aging lung. To identify robust druggable protein targets, we propose a principled causal framework that makes use of multiple data modalities. Our analysis highlights the importance of serine/threonine and tyrosine kinases as potential targets that intersect the SARS-CoV-2 and aging pathways. By integrating transcriptomic, proteomic and structural data that is available for many diseases, our drug discovery platform is broadly applicable. Rigorous in vitro experiments as well as clinical trials are needed to validate the identified candidate drugs. |
|
Neha Prasad, Karren Yang, Caroline Uhler ICML Workshop on Computational Biology, 2020 (Oral Spotlight) We propose a novel approach to computational lineage tracing that combines supervised learning with optimal transport based on generative adversarial networks. pdf | abstract | codeIn this paper, we present Super-OT, a novel approach to computational lineage tracing that combines a supervised learning framework with optimal transport based on Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs). Unlike previous approaches to lineage tracing, Super-OT has the flexibility to integrate paired data. We benchmark Super-OT based on single-cell RNA-seq data against Waddington-OT, a popular approach for lineage tracing that also employs optimal transport. We show that Super-OT achieves gains over Waddington-OT in predicting the class outcome of cells during differentiation, since it allows the integration of additional information during training. |

|
Karren Yang, Caroline Uhler ICLR, 2019 We align and translate between datasets by performing unbalanced optimal transport with generative adversarial networks. pdf | abstract | codeGenerative adversarial networks (GANs) are an expressive class of neural generative models with tremendous success in modeling high-dimensional continuous measures. In this paper, we present a scalable method for unbalanced optimal transport (OT) based on the generative-adversarial framework. We formulate unbalanced OT as a problem of simultaneously learning a transport map and a scaling factor that push a source measure to a target measure in a cost-optimal manner. In addition, we propose an algorithm for solving this problem based on stochastic alternating gradient updates, similar in practice to GANs. We also provide theoretical justification for this formulation, showing that it is closely related to an existing static formulation by Liero et al. (2018), and perform numerical experiments demonstrating how this methodology can be applied to population modeling. |
|
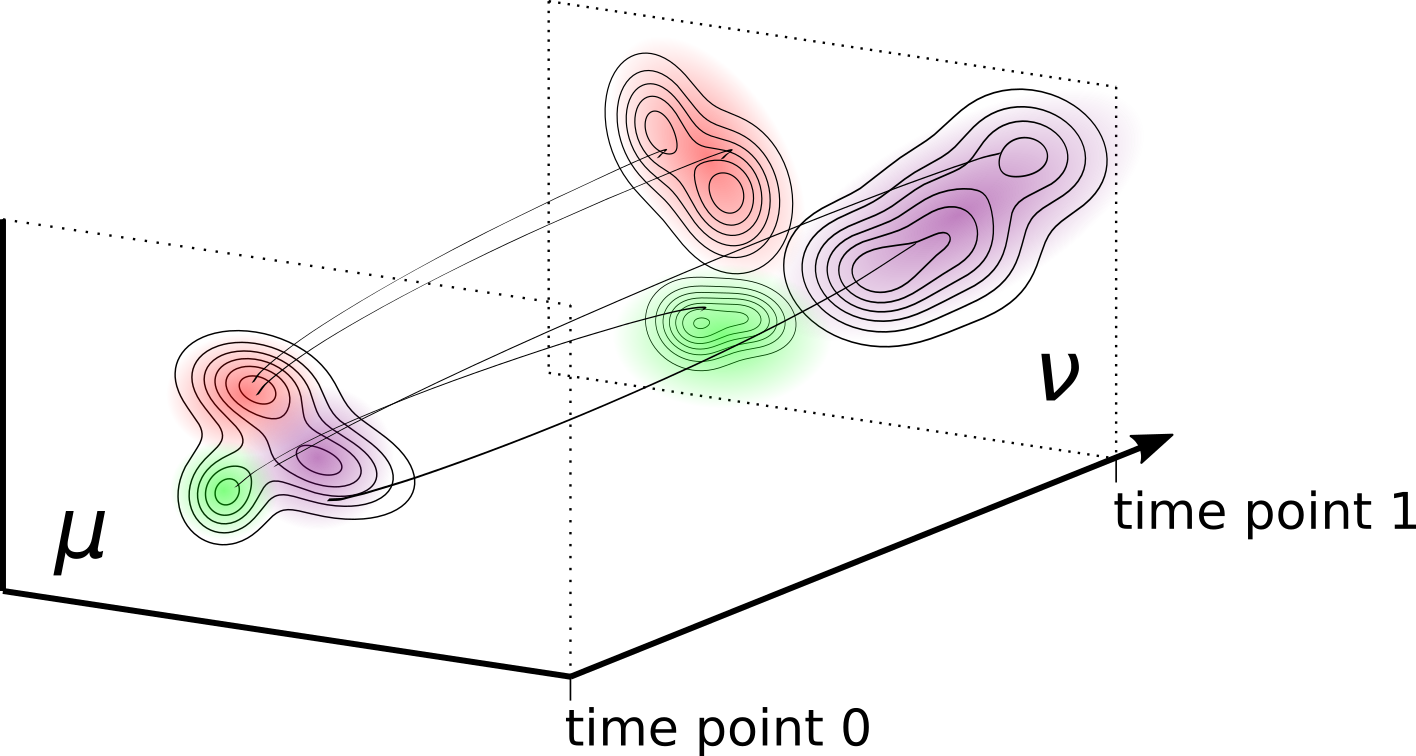
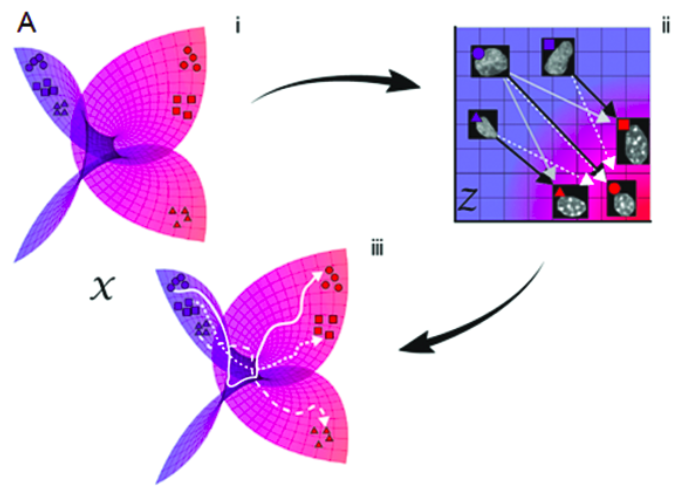
Karren Yang, Karthik Damodaran, Saradha Venkatachalapathy, Ali C. Soylemezoglu, G. V. Shivashankar, Caroline Uhler PLOS Computational Biology 16(4): e1007828 (2020) We combine autoencoding and optimal transport to align biological imaging datasets collected from different time points. pdf | abstract | codeLineage tracing involves the identification of all ancestors and descendants of a given cell, and is an important tool for studying biological processes such as development and disease progression. However, in many settings, controlled time-course experiments are not feasible, for example when working with tissue samples from patients. Here we present ImageAEOT, a computational pipeline based on autoencoders and optimal transport for predicting the lineages of cells using time-labeled datasets from different stages of a cellular process. Given a single-cell image from one of the stages, ImageAEOT generates an artificial lineage of this cell based on the population characteristics of the other stages. These lineages can be used to connect subpopulations of cells through the different stages and identify image-based features and biomarkers underlying the biological process. To validate our method, we apply ImageAEOT to a benchmark task based on nuclear and chromatin images during the activation of fibroblasts by tumor cells in engineered 3D tissues. We further validate ImageAEOT on chromatin images of various breast cancer cell lines and human tissue samples, thereby linking alterations in chromatin condensation patterns to different stages of tumor progression. Our results demonstrate the promise of computational methods based on autoencoding and optimal transport principles for lineage tracing in settings where existing experimental strategies cannot be used. |
|
Karren Yang, Caroline Uhler ICML Workshop on Computational Biology, 2019 (Oral Spotlight) We train domain-specific autoencoders to map different data modalities to the same latent space and translate between them. pdf | abstractMulti-domain translation seeks to learn a probabilistic coupling between marginal distributions that reflects the correspondence between different domains. We assume that data from different domains are generated from a shared latent representation based on a structural equation model. Under this assumption, we show that the problem of computing a probabilistic coupling between marginals is equivalent to learning multiple uncoupled autoencoders that embed to a given shared latent distribution. In addition, we propose a new framework and algorithm for multi-domain translation based on learning the shared latent distribution and training autoencoders under distributional constraints. A key practical advantage of our framework is that new autoencoders (i.e., new domains) can be added sequentially to the model without retraining on the other domains, which we demonstrate experimentally on image as well as genomics datasets. |
|
Raj Agrawal, Chandler Squires, Karren Yang, Karthik Shanmugam, Caroline Uhler AISTATS, 2019 We propose an experimental design strategy for target causal discovery. pdf | abstract | codeDetermining the causal structure of a set of variables is critical for both scientific inquiry and decision-making. However, this is often challenging in practice due to limited interventional data. Given that randomized experiments are usually expensive to perform, we propose a general framework and theory based on optimal Bayesian experimental design to select experiments for targeted causal discovery. That is, we assume the experimenter is interested in learning some function of the unknown graph (e.g., all descendants of a target node) subject to design constraints such as limits on the number of samples and rounds of experimentation. While it is in general computationally intractable to select an optimal experimental design strategy, we provide a tractable implementation with provable guarantees on both approximation and optimization quality based on submodularity. We evaluate the efficacy of our proposed method on both synthetic and real datasets, thereby demonstrating that our method realizes considerable performance gains over baseline strategies such as random sampling. |
|
Karren Yang, Abigail Katcoff, Caroline Uhler ICML, 2018 (Oral Presentation) We characterize interventional Markov equivalence classes of DAGs that can be identified under soft interventions and propose the first provably consistent algorithm for learning DAGs in this setting. pdf | abstractWe consider the problem of learning causal DAGs in the setting where both observational and interventional data is available. This setting is common in biology, where gene regulatory networks can be intervened on using chemical reagents or gene deletions. Hauser and Bühlmann (2012) previously characterized the identifiability of causal DAGs under perfect interventions, which eliminate dependencies between targeted variables and their direct causes. In this paper, we extend these identifiability results to general interventions, which may modify the dependencies between targeted variables and their causes without eliminating them. We define and characterize the interventional Markov equivalence class that can be identified from general (not necessarily perfect) intervention experiments. We also propose the first provably consistent algorithm for learning DAGs in this setting and evaluate our algorithm on simulated and biological datasets. |

|
Adityanarayanan Radhakrishnan, Karren Yang, Mikhail Belkin, Caroline Uhler arXiv, 2018 We show that overparameterized autoencoders are biased towards learning step function around training examples. pdf | abstractThe ability of deep neural networks to generalize well in the overparameterized regime has become a subject of significant research interest. We show that overparameterized autoencoders exhibit memorization, a form of inductive bias that constrains the functions learned through the optimization process to concentrate around the training examples, although the network could in principle represent a much larger function class. In particular, we prove that single-layer fully-connected autoencoders project data onto the (nonlinear) span of the training examples. In addition, we show that deep fully-connected autoencoders learn a map that is locally contractive at the training examples, and hence iterating the autoencoder results in convergence to the training examples. Finally, we prove that depth is necessary and provide empirical evidence that it is also sufficient for memorization in convolutional autoencoders. Understanding this inductive bias may shed light on the generalization properties of overparametrized deep neural networks that are currently unexplained by classical statistical theory. |
|
Yuhao Wang, Liam Solus, Karren Yang, Caroline Uhler NeurIPS, 2017 (Oral Presentation) We present two provably consistent algorithms for learning DAGs from observational and (hard) interventional data. pdf | abstractLearning directed acyclic graphs using both observational and interventional data is now a fundamentally important problem due to recent technological developments in genomics that generate such single-cell gene expression data at a very large scale. In order to utilize this data for learning gene regulatory networks, efficient and reliable causal inference algorithms are needed that can make use of both observational and interventional data. In this paper, we present two algorithms of this type and prove that both are consistent under the faithfulness assumption. These algorithms are interventional adaptations of the Greedy SP algorithm and are the first algorithms using both observational and interventional data with consistency guarantees. Moreover, these algorithms have the advantage that they are nonparametric, which makes them useful also for analyzing non-Gaussian data. In this paper, we present these two algorithms and their consistency guarantees, and we analyze their performance on simulated data, protein signaling data, and single-cell gene expression data. |
|
|